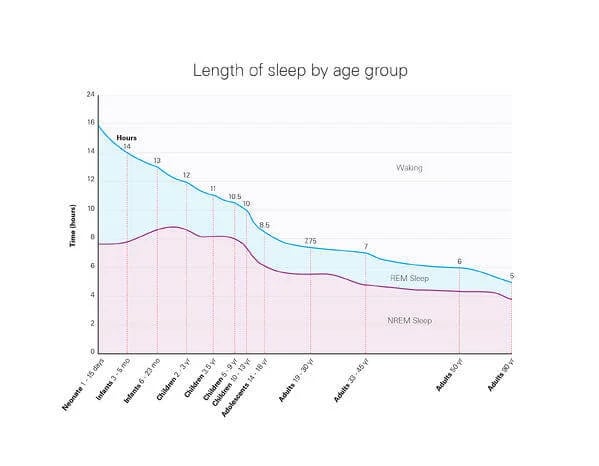
REM sleep
Your first period of REM sleep (when you’re most likely to dream) usually takes place about an hour and a half after falling asleep. If someone looked at you while you were in REM sleep, they’d notice that your eyes are moving rapidly from side to side behind your closed lids. Your brain waves change and resemble the brain waves seen when you’re awake. You breathe faster, and your pulse increases. If you are woken during REM sleep, you may remember your dream.
During the night your brain will cycle through these sleep phases, favouring REM sleep and lighter sleep as you approach morning.